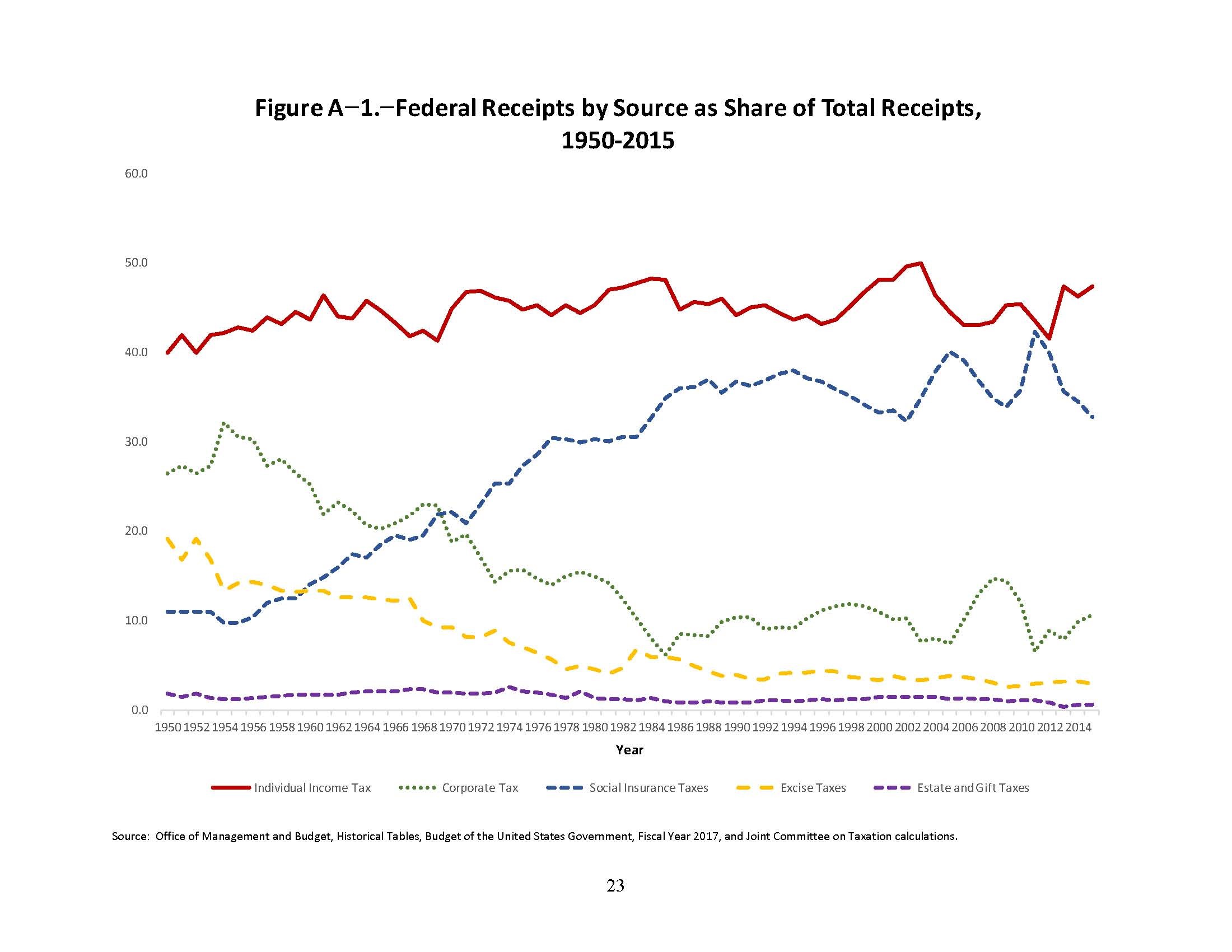
Should the US Lower Tax Rates on US Multi-National Corporations?
/Should the US lower its tax rates to allow US multi-national corporations (USMNCs) to repatriate earnings allegedly re-invested offshore?
In the news, several USMNCs are lobbying the President and Congress to further lower the tax rate on repatriation of earnings allegedly re-invested in offshore operations that was proposed by the White House to be taxed at 15%. This Reuter's Article, suggests that the USMNCs are seeking to lower the current 35% tax rate on repatriation of earnings to 3.5% tax rate on earnings already invested abroad in illiquid assets, such as factories, and 8.75% tax rate on earnings cash and liquid assets.
The Reuter's article speculates that the repatriated earnings/cash and taxes raised from the repatriated earnings/cash could raise tax revenues and funds the expansion of the US economy: "If the $2.6 trillion overseas were repatriated at once, two things would happen. First, Washington would get a big jolt of tax revenue. Second, repatriated profits not collected by the Internal Revenue Service could be put to use in the economy."
The last time the US had a "tax repatriation holiday" was in 2004-2005, and the results of the tax repatriation holiday show that the alleged reinvestment into the US economy by the USMNCs that took advantage of the 5.25% lowered rate on the repatriation of earnings did not occur. In 2001, as noted in the Reuter's article, the Senate held a hearing into the effects of the 2004 repatriation holiday and determined that the repatriation cost the US treasury at least $3.3 billion in net revenue over 10 years and produced no appreciable increase in U.S. jobs or domestic investment. Instead, the repatriated funds were used to buy back shares and to pay executive bonuses.
Finally, the Reuter's article notes that this may be an effort of lobbyists for the USMNCs to signal the log fight ahead to achieve the new repatriation tax holiday by initially setting the percentages low, and therefore reaching a "compromise" at a slightly higher percentage.
The Reuter's article raises a fundamental question, namely: Should Congress and the President be considering passing tax reform implementing a reduced tax rate for the repatriation of earnings, or should we be looking at other ways to reform the current corporate tax "imbalance" problems, when there are no benefits (as reflected in the most recent tax repatriation holiday)?
This Bloomberg article suggests that the benefits of a tax repatriation holiday touted by USMNCs are just myths as follows:
- The article stats by quoting Trump's economic advisor touting that the repatriation of earnings will cause a boost to the U.S. economy. Contrast this statement with the Senate PSI findings of fact in its 2001 study on the 2004 tax repatriation holiday, where the Senate PSI determined that after repatriation over $150 billion dollars, the top 15 USMNCs actually reduced its workforce by 20,931 jobs. Also there was no new R&D expenditure by the top 15 USMNCs that took advantage of the tax repatriation.
- The article then states that companies have been borrowing funds in the US at historic rates and that any perceived additional tax revenues would have to be low enough to incentivize the companies to forego borrowing the money and repatriating the offshore earnings/funds. Contrast this point with the Senate PSI findings that the repatriation holiday actually reduced tax collection by $3.3 billion over 10 years, and leads to the conclusion that a tax repatriation holiday would not generate tax revenue because the tax rate would have to be so low, and historically speaking there would be a net loss over 10 years of taxable revenue attributable to the tax holiday.
- The article points out that the borrowed funds by USMNCs have been used for stock buy backs and executive bonuses. Compare the use of the repatriated funds from the 2004 tax holiday which were almost exclusively used to fund stock buy backs and executive compensation with the current use of borrowed funds by the top USMNCs and this suggests that any repatriation holiday will continue this trend.
- Finally, the article points out that clearing a supposed hurdle to the repatriation of offshore earnings (lowering the tax rate) may not incentivize USMNCs to repatriate the funds because they have operations overseas, or may continue to benefit from the sequestering of offshore earnings in lower tax jurisdiction. Compare this myth with the Senate PSI findings that post 2004, more USMNCs increased, not decreased, their offshore earnings accumulation rate.
Both articles suggest that repatriation of offshore earnings at a lower rate for USMNCs, when coupled with the Senate PSI findings, reflect unsound US tax policy. However, it appears as if Congress and the White House continue to buy into the myth that the USMNCs are perpetuating that a repatriation tax holiday is the remedy that will increase the US economy, generate more US tax dollars and spur economic growth. Despite the message the USMNCs are sending, Congress and the President should look at historical data to see that the myth of a one quick fix solution (repatriation tax holiday) is a failure.
If you know of any company or individual that has sheltered funds offshore, and would like assistance in assessing and filing your IRS whistleblower claim, please CONTACT US. The IRS Whistleblower Program pays between 15-30% if collected proceeds when the IRS proceeds based on a whistleblower's substantial and credible information.